The interview question
Imagine you were a university student looking to land an entry-level software engineer job and you were having this technical coding interview. The interview question starts with a table showing amount of units of a product sold at the shop and the corresponding price per unit. The idea here is that there is an incentive for customers to buy in bulk – the more we can sell the lower the price:
purchase quantity price per unit
1-5 5 dollars
6-10 4 dollars
11-20 3 dollars
20+ 2.5 dollars
The task the interviewer asks you to do is to write out a function that takes the amount of the times being purchased as the input and output the price per unit according the table. So if the input is 5, the function returns 5, and if the input is 6, the function returns 4... you get the idea.
That's it. That is the whole question. "This is even simpler than Fizz Buzz," you think to yourself, "but it might lead to more difficult follow-up questions, like it might get tweaked into a binary search problem or something". So you start to write the following simple solution, expecting more in-depth follow-up questions to come.
function getPrice(amount) {
if (amount >= 1 && amount <= 5) return '5';
if (amount >= 6 && amount <= 10) return '4';
if (amount >= 11 && amount <= 20) return '3';
if (amount > 21) return '2.5';
return 'unknown price';
}
However, to your surprise, after you came up with this solution, the interviewer just stops there, moves on to the next question or discusss something completely unrelated.
The next day, you get a rejection letter from the company.
The Tweet
This is based off of a true story. It was a real interview question and the solution I wrote above was considered unacceptable by the interviewer, i.e. the tweet author.
#微代码 最近面试校招生的一个感想:有非常多的同学会写出解法1的代码,这让我很难理解。以至于只要看到有解法2的样子,印象上就会先加分了。 pic.twitter.com/g38d2A5Bjj
— toobug (@TooooooBug) September 13, 2021
A while ago this tweet went viral in the Chinese programming circle. The tweet author used this exact question to screen new grads for an entry-level software engineer position. The tweet and the question were written in Chinese so I translated this question into English.
In the tweet, he complained that he was having a hard time understanding (很难理解) why many students came up with the solution that we came up with above. Instead of a straightforward solution with a bunch of if statements, he said he was expecting an answer like this:
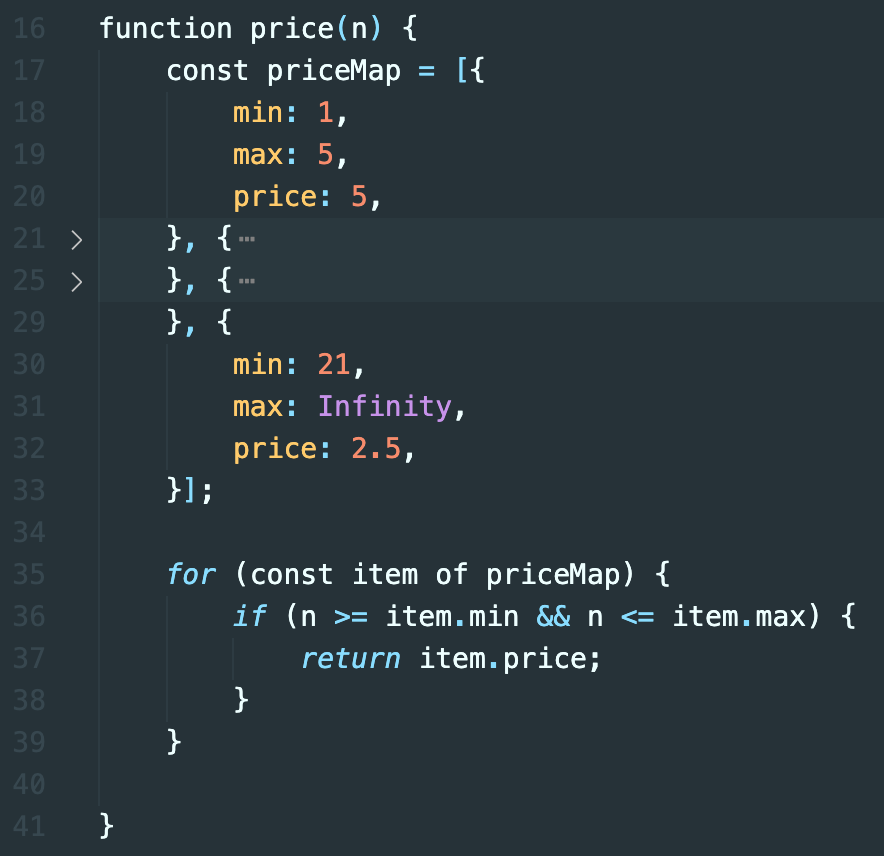
Compared to the first solution with a bunch of if statements, this solution, in his opinion, is more modular, extensible, and maintainable. That was the answer he had in mind and failing to arrive at this solution means you are weeded out in the interview process.
I am not sure how you feel about this, but in my opinion, this is a pretty pointless interview question to ask new grads. The first solution is totally fine. Under the right circumstances, the second solution is closer to what you would want in production code, even though it is still not quite the table-driven development you'd want.
There are so many things I want to unpack, so here is the tl;dr:
- Different types/styles of interviews call for different answers and that should be clearly communicated during the interview. The first solution is totally fine as the answer to an algorithmic question.
- Take control of your interview so you don't have to guess what the interviewer has in mind. You do this by asking clarifying questions. Keep asking until everything the interviewer is looking for is clear to you.
- The table-driven method (what the second solution tries to achieve) optimizes for changes and that's why the interviewer (the tweet author) failed students who didn't come up with that answer.
The overarching theme in this post is that you should take control of your coding interview so you don't have to guess the answer your interviewer is thinking of.
Different styles of interviews calls for different answers
Generally, there are two types of coding interviews:
- Interviews that focus on algorithms & data structures
- Interviews that focus on practical app/feature-building and test your hands-on engineering chops
Normally it should be easy to distinguish between these two types of interviews by merely looking at the question: Inverting a Binary Tree is a typical algorithmic question, while designing and implementing an auto-complete search feature is more about practical app-building. Although sometimes the two types of interview questions would blend. For example, you might be asked to (partially) implement a trie when you are talking about the design of an auto-complete search feature/service/component. But these two different types of interviews are meant to test different competences.
In a pure algorithmic, LeetCode-type of interviews, your main goal is to leverage the right data structures and come up with an efficient algorithm to solve the problem with the right set of memory/runtime complexity trade-offs as fast as you can. How readable, maintainable and extensible your code is, or whether it conforms to the current best practice in the the community/industry are not that important, or at least secondary to the main goal. You can go ahead and name your variables i, n, p, q and mutate that input array in-place without being judged as long as your solution passes the test cases under the time and memory limits.
As Joel Spolsky wrote in his blog post: with the algorithmic interview questions, he wants to see if the candidate is smart enough to "rip through a recursive algorithm in seconds, or implement linked-list manipulation functions using pointers as fast as you can write on the whiteboard".
For more experienced engineers/developers, the coding interview tends to lean into the practical app-building category, where readable, maintainable code and extensible program structure are what they look for, and all aspects of the full software development life cycle, even including error handling, are fair game to be asked, as they are important in real-world software building.
Here I don't make any value judgment about which type of interviews are good or better. I just pointed out that they exist and interviewers look for different things by conducting different types of interviews.
Take control over the interview
As an interviewee, you want to make sure you understand which category the question falls into because the underlying core criteria on which you are assessed are different – you don't want to overload the capacity of the working memory of your brain with tasks that are secondary before you reach the main goal. You want to take control over the interview so you are not left in the dark.
One way to take control over the interview is to narrate your thoughts as you go and articulate any assumptions you have to make sure you get confirmation from your interviewer on your way forward or they should help you correct course.
If I were the candidate receiving this exact question, I would ask this upfront: "should I write production-grade code with good engineering practices or you are more interested in how I'd tackle the algorithm & data structure part?". That is probably one of the highest ROI questions we can ask during an interview. The interviewer would either tell me to write a workable solution under the constraints of the runtime or space characteristics or treat this as a real-world engineering problem with real-world tradeoffs.
With all that being said, it is a bad question to ask new grads
The question itself doesn't test any of the core competencies that distinguish between brilliant programmers and mediocre ones. What's really being tested here, based on the (ideal) answer the interviewer (the author of the tweet) had in mind, is the whether the candidate – new CS grads without any significant experience working in the software industry – knows how to use the table-driven method to implement such a function.
I don't believe that any smart college student who can breeze through a graph traversal problem in an interview can't understand and pick up patterns like the table-driven method in just a couple of hours. On the other hand, any mediocre programmers who happened to read Code Complete can write a table-driven solution and pass the interview. Not to say that knowing good engineering practices is not a good thing; it is just that using that as the only hiring criteria to hire new grads is pointless and it doesn't help you find the smart kids.
So what are the ideal interview quetsions to ask new grads?
Joel pointed it out in his post that the ideal interview questions should cover at least one of these two Computer Science concepts: 1. recursion 2. pointers
I actually agree with him on this. You want to ask questions about these two concepts not because they are ubiquitous in your average codebase and you have to use them every day. It is because they are a great tool to test the ability to reason and think in abstractions, the kind of mental aptitude a brilliant programmer would have.
Anyway, the moral of the story is don't be afraid to ask clarifying questions so you don't have to guess what the interviewer looks for and cares about if they are not being explicit about their expectations.
You can stop here if you don't care about technical discussions about this simple interview question.
Table-driven development
Solution 2 resembles a form of table-driven development described in a classic programming book called Code Complete. But even if you have never read the book, you probably know this pattern from your experience working as a software developer/engineer.
At its core, it tries to separate data from logic: instead of having all the information about pricing strategy (the data) hardcoded in the function (the logic) as literal values, it separates them.
The pricing strategy is a business rule, and business rules tend to be the source of frequent changes. By encoding that in an external data structure (i.e. the array priceMap in this case), we make our program easier to accommodate future changes. Whenever the pricing strategy changes, we can just modify the entries in the array without touching the logic of the function. In other words, we isolate the unstable part, so the effect of a change will be limited.
However, I said it only resembles table-driven development that you'd use in production code but it is not quite there yet:
- The pricing data is not fully separated from the logic as the array
priceMapis still defined within the function - Magic numbers are still there
Depending on where the pricing data comes from, one possible variation of the table-driven method for this particular question is as follows:
// config.js
export const priceByRanges = [
{min: 1, max: 5, price: '5'},
{min: 6, max: 10, price: '4'},
{min: 11, max: 20, price: '3'},
{min: 21, max: Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER, price: '2.5'},
];
// app.js
import {priceByRanges} from './config.js';
function getPrice(amount) {
// error handling for amount outside the range
return priceByRanges.find(
(priceByRange) => amount >= priceByRange.min && amount <= priceByRange.max,
).price;
}
Now the pricing data is stored in config.js seperately and priceByRanges is resolved at load time.
Further optimization
If the array priceByRanges is always sorted in terms of the price ranges, we can further optimize Solution 2 by leveraging binary search.
const priceByRanges = [
{min: 1, max: 5, price: '5'},
{min: 6, max: 10, price: '4'},
{min: 11, max: 20, price: '3'},
{min: 21, max: Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER, price: '2.5'},
];
function getPrice(amount) {
if (amount < priceByRanges[0].min) {
return 'unknown price';
}
let start = 0,
end = priceByRanges.length - 1;
while (start <= end) {
const mid = (start + end) >>> 1;
if (priceByRanges[mid].max < amount) {
start = mid + 1;
} else {
end = mid - 1;
}
}
return priceByRanges[start].price;
}
What is this >>>?
>>> is binary right shift by 1 position, which is effectively just a division by 2 followed with a Math.floor. e.g. for 11: 1011 -> 101 results to 5.
Notes on performance and Big O
It might feel that the first clumsy solution with a bunch of if blocks is better in terms of the performance than the second table-driven approach that loops through the array.
Actually for the Big O analysis, both approaches have the same constant time complexity, as the number of operations (i.e. comparision between amount and the price range), doesn't grow no matter how big the input is (i.e. amount).
What's more interesting, in my opinion, is the performance implications between using a loop vs. "unrolling" the loop. By unrolling I mean discretely writing line-by-line of the loop body. A quick google search suggests that popular JavaScript engines such as V8 heavily optimize loops. But getting any accurate results from such a micro-benchmarking is really hard as the performance varies a lot depending on different factors like the engine and the code in the loop body.